Abstract and Introduction
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
Combining genetic variants increasing risk of dementia and cardiovascular risk factors can facilitate identification of high-risk individuals for targeted prevention of dementia. Identification of high-risk individuals is warranted since only intensive and thereby expensive multidomain intervention trials, targeting primarily cardiovascular risk factors, show improved cognition in individuals at risk of dementia.
Dementia is a major global challenge for health and social care in the 21st century. A third of individuals >65 years of age die with dementia, and worldwide incidence numbers are projected to be higher than 150 million by 2050. Dementia is, however, not an inevitable consequence of old age; 40% of dementia may theoretically be preventable. Alzheimer's disease (AD) accounts for approximately two-thirds of dementia cases and the major pathological hallmark of AD is accumulation of amyloid-β. Nevertheless, the exact pathological mechanisms of AD remain unknown. Cardiovascular disease and dementia share several risk factors and dementia often coexists with cerebrovascular disease. In a public health perspective, prevention is crucial, and it is suggested that a 10% reduction in prevalence of cardiovascular risk factors could prevent more than nine million dementia cases worldwide by 2050. Yet this assumes causality between cardiovascular risk factors and dementia and adherence to the interventions over decades for a large number of individuals. Using genome-wide association studies, the entire genome can be scanned for disease/trait associated loci in a hypothesis-free manner, and the compiled genetic information is not only useful for pinpointing novel pathogenic pathways but also for risk assessments. This enables identification of individuals at high risk, who likely will benefit the most from a targeted intervention. Further optimization of the risk stratification can be done by adding cardiovascular risk factors. Additional studies are, however, highly needed to elucidate dementia pathogenesis and potential shared causal risk factors between cardiovascular disease and dementia.
Introduction
Treatment and prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (CVD) and other common diseases have been highly successful during the past decades, and people now live long enough to develop age-dependent dementia disorders. Therefore, dementia has become a major global challenge for health and social care in the 21st century. A third of people >65 years of age now die with dementia,[1,2] and worldwide incidence numbers are projected to be higher than 150 million by 2050.[2,3] Dementia is, however, not an inevitable consequence of old ages, and 40% of dementia is estimated to be preventable.[1,2,4] Incidences are declining in the western part of the world,[5–10] caused partly by improved control of cardiovascular risk factors, increased educational level, and awareness of the importance of a healthy lifestyle.[1,2,4,5,7–11] It is suggested that a 10% reduction in prevalence of cardiovascular risk factors could prevent more than nine million dementia cases worldwide by 2050.[4]
Dementia is a syndrome of gradual decline in mental ability severe enough to interfere with activities of daily living.[12] Most often dementia neuropathology develops over decades before symptoms appear. The classical symptoms are decline in memory, especially short-term, decline in reasoning, or altered behaviour. The cognitive decline is gradual without clear cut transitions, and clinically the syndrome is divided into mild, moderate, and severe dementia. Early-onset dementias (<65 years of age) account for <10% of all dementia cases and include rare Mendelian forms.[12,13] Alzheimer's disease (AD) accounts for approximately two-thirds of late-onset dementia (>65 years of age)[3,14,15] and also harbours a significant genetic component, the most important being APOE (apolipoprotein E gene). Carriers of the APOE ɛ4 allele have increased risk of AD compared to carriers of ɛ33 (wild type), with an 8- to 15-fold increased risk in ɛ44 homozygote individuals.[16,17] However, large parts of the biology leading to dementia remain unknown, and there are no curative or truly relieving treatments. To help discover novel pathogenic pathways and thus new molecules for drug targets, genome-wide association studies (GWAS) can be useful instruments.[18,19] By this, the entire genome can be scanned for disease/trait associated loci in a hypothesis-free manner. The compiled genetic information is not only useful for pinpointing novel pathogenic pathways but also for risk assessments. It can enable identification of individuals at high risk, who have not yet developed dementia pathology and thus enable targeted early interventions towards those that will benefit the most.[20,21]
Recently, it has become apparent that CVD and dementia share several risk factors.[1,2] Intervention studies are primarily targeting cardiovascular risk factors in individuals above 65 years of age. Only the very intense interventions, however, seem to yield benefit.[22–25] This highlights the need for identification of which pathogenic pathways and specific risk factors that will be most efficient to target with preventive and/or pharmacological interventions.[1,2]
The aim of this review is dual: first, we want to summarize the potential cardiovascular causes of dementia, and, second, we want to determine whether dementia risk prediction can be optimized by combining genetics and cardiovascular risk factors.
Literature Search
A systematic literature search of the PubMed database (20 June to 5 July 2022) was performed using the advanced search feature asking for titles and/or abstracts containing either 'Alzheimer's disease', 'Alzheimer', 'dementia', 'vascular dementia' or 'mixed dementia' AND 'pathogenesis', 'pathology', 'genetics', 'genome-wide association study' or 'GWAS' for the section on Epidemiology, aetiology, and genetics of dementia. For the section on modifiable risk factors in dementia, the terms 'dementia', 'Alzheimer's disease', 'Alzheimer', 'vascular dementia', 'cognition' or 'cognitive decline' AND 'diabetes', 'obesity', 'BMI', 'body mass index', 'hypertension', 'blood pressure', 'physical activity', 'physical inactivity', 'education', or 'smoking' AND 'meta-analysis' or 'Mendelian randomization' were used. For the section on risk prediction in dementia, the terms 'Alzheimer's disease', 'Alzheimer', 'dementia' or 'vascular dementia', AND 'risk score', 'polygenic risk score', 'PRS' or 'risk assessment' were used.
Epidemiology, Aetiology, Genetics, and Diagnosis of Dementia
Dementia in Numbers. Worldwide it is estimated that more than 50 million individuals suffer from dementia, and while AD is the most abundant form, one-third is caused by vascular, mixed, or unspecified dementia and often collectively called 'non-Alzheimer's dementia'.[3,14,15]
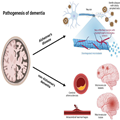
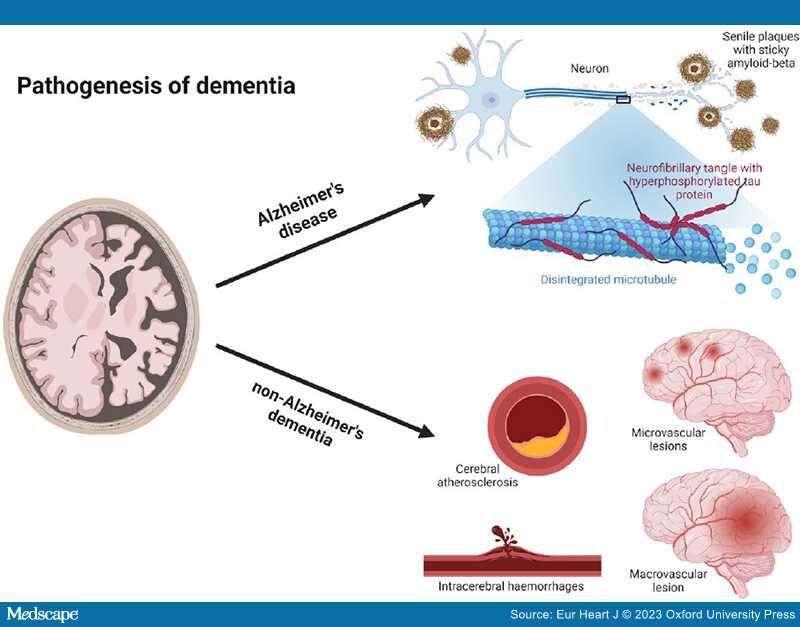
Pathogenesis of Alzheimer's Disease. Alzheimer's disease was first described in 1907 by Alois Alzheimer.[26] He described a 51-year-old patient with clear clinical signs of dementia and post-mortem characteristic changes still considered part of the neuropathological hallmarks of AD.[26] The neuropathological hallmarks of AD are senile plaques of the sticky amyloid-β peptide, neurofibrillary tangles composed of hyperphosphorylated tau protein, neuronal damage, and cell death leading to atrophy of affected brain areas[27] (Figure 1). However, the true toxic components of AD are still debated; accumulation of amyloid-β and senile plaques correlates poorly with cognitive decline, is shown to begin decades before clinical symptoms,[28,29] and is also found in cognitively normal elderly individuals.[30–32] Tau pathology is shown to correlate better with cognitive decline,[33] and neuronal loss correlates the best with cognitive decline in AD.[34,35] More recently, it has been suggested that microglia, constituting the innate immune system of the brain,[36,37] are activated by the accumulation of amyloid-β and tau proteins to phagocytose the toxic proteins. When microglia cannot meet the excess of toxic proteins, chronic inflammation is thought to evolve[38] switching microglia into the proinflammatory state mediating neurotoxicity through cytokine release and engulfment of neuronal synapses, hence leading to progression of AD pathology.[39,40] An alternative suggestion is that the main driver of AD pathogenesis is focal adhesion defects in synapses with multiple entry points ultimately leading to synaptic dysregulation and consequently synapse loss and cognitive decline.[14]
Figure 1.
Pathogenesis of dementia. Dementia can be divided into two major groups, Alzheimer's disease and non-Alzheimer's dementia. Neuropathologically Alzheimer's disease is characterized by senile plaques of the sticky amyloid-β peptide, neurofibrillary tangles composed of hyperphosphorylated tau protein, neuronal damage, and cell death leading to atrophy of affected brain areas. Non-Alzheimer's dementia is primarily caused by various vascular pathology. Both cerebral atherosclerosis, microvascular, and macrovascular lesions can cause oxidative stress and inflammation, induce cerebral hypoperfusion, and thereby lead to brain atrophy and neurodegeneration of affected areas. Figure created with biorender.com.
The Genetic Story of AD From Early-onset to Late-onset, From 1930s to 2030s. In the 1930s, studies in early-onset AD pedigrees revealed an autosomal dominant mode of inheritance.[41] It was, however, not until the 1980s and 1990s that candidate genes were discovered. APP (amyloid precursor protein gene), located at the long arm of chromosome 21,[42–44] was identified after the discovery of a strong homology between the amyloid-β peptides, isolated from brains of AD patients and Down syndrome patients who possess an extra copy of chromosome 21.[45–47] Further studies in APP-negative pedigrees identified PSEN1 (presenilin 1 gene) and PSEN2 (presenilin 2 gene).[48,49] Both proteins are part of the γ-secretase complex that cleaves amyloid precursor protein into amyloid-β.[50] Despite the similarities in neuropathology, the similar associations were not found for late-onset AD.[51] In 1993, APOE was the first gene described to be associated with late-onset AD.[16,17]APOE is located on chromosome 19 and has three common alleles, ɛ2, ɛ3, and ɛ4[52] where ɛ4 is associated with increased risk of late-onset AD. The ɛ3 allele is considered the wild type with an allele frequency in Northern Europeans of 75%–80%.[53,54] ApoE is primarily produced in the liver and in astrocytes in the brain.[55,56] Outside the brain apoE is mainly contained in triglyceride-rich lipoproteins and has an important role in lipid transport and metabolism,[57,58] and in the brain, apoE is the major apolipoprotein and lipid transporter.[59,60] The first two GWAS studies on AD was published in 2007 confirming the association of APOE ɛ4 and disease.[61,62] Since then, 75 loci have been identified to be associated with AD through traditional GWAS studies[63–65] as well as through exome and whole-genome sequencing.[14,66,67]
Pathogenesis of Non-Alzheimer's Dementia. Non-Alzheimer's dementia is primarily caused by vascular pathology in and around the cerebral vessels. Because AD and cerebrovascular disease commonly coexist, it is often difficult to ascribe accurately the relative contributions of each to an individual's cognitive decline. Consequently, clinicians should ensure that substantial vascular changes are present if dementia is to be attributed entirely to vascular pathology.[1,2] The vascular burden also has to be located feasibly to account for the clinical symptoms and be considered clinically significant, which is defined as either many lacunae, strategic infarcts, a substantial burden (>25%) of white matter lesions, or a combination of these.[1,2,68,69] Cerebral atherosclerosis, microvascular and macrovascular lesions can cause oxidative stress, inflammation, induce cerebral hypoperfusion and thereby lead to brain atrophy and neurodegeneration of affected areas[1,2,69,70] (Figure 1). The presentation can be abrupt when caused by a larger stroke or intracerebral haemorrhages, or insidious over years when caused by lacunar and micro infarcts, intracerebral haemorrhages, microbleeds, and white matter lesions.[68,71] The clinical symptoms are dependent on the location of the pathology.
Diagnosis of Dementia. The diagnosis of dementia is based on medical history, physical and neurological examination, cognitive assessment, psychological assessment, assessment of activities of daily living, blood samples, structural brain scan, and assessment of differential diagnoses as detailed in the Supplementary material online, The diagnosis of dementia and Table S1.
Modifiable Risk Factors in Dementia
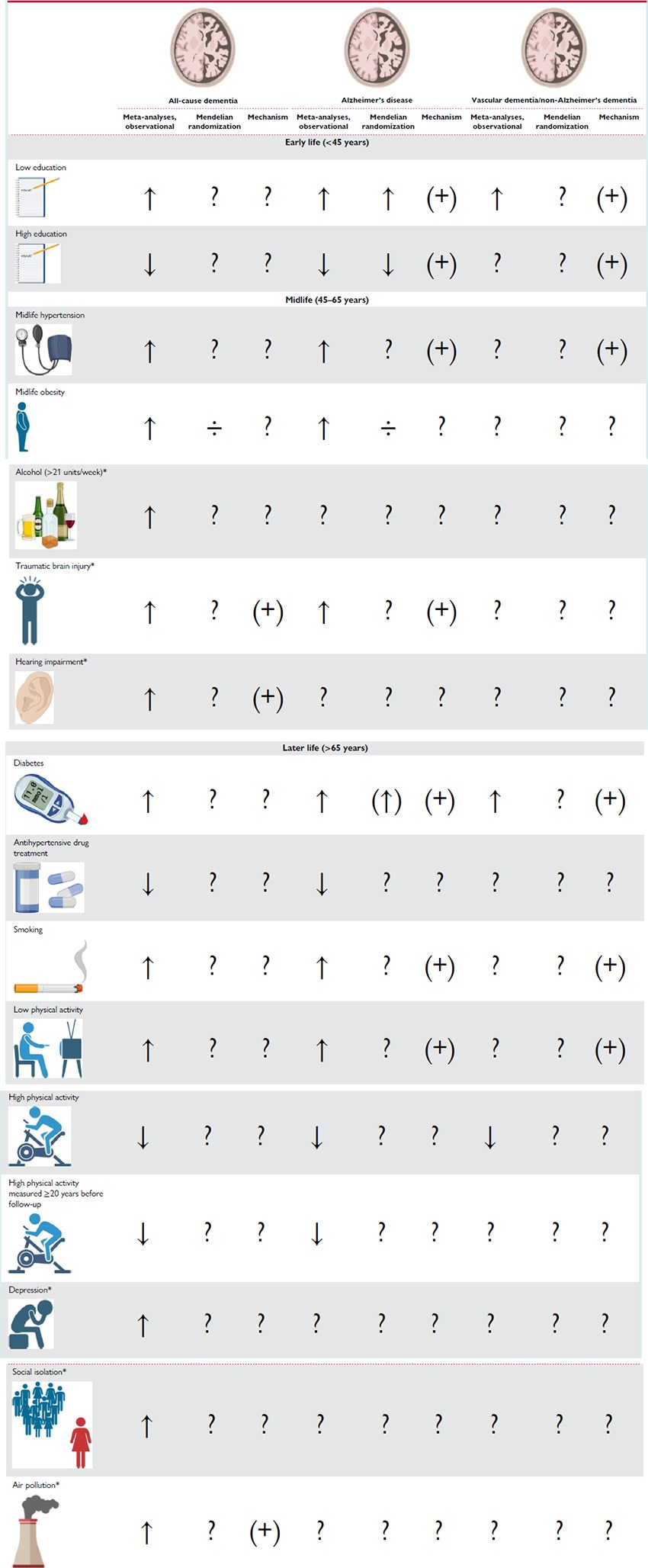
Background. Age is by far the strongest risk factor for dementia,[38,72] and a family history of AD is also a major risk factor.[73,74] None of these are, however, modifiable. During the last decades, it has become clear that modifiable lifestyle factors also influence dementia risk, although it is not clear whether modifiable risk factors influence all types of dementia.[1,2] The vast part of the literature on modifiable risk factors addresses dementia in general and not dementia subtypes. The Lancet Commission 2020 Report on Dementia lists 12 modifiable risk factors associated with dementia, half of them being cardiovascular and the remaining being traumatic brain injury, hearing impairment, depression, social isolation, and air pollution[2] (Table 1).
A major problem in studies of cardiovascular risk factors and endpoints occurring in very old ages as dementia is survivor selection bias. The inevitable selection of survivors of cardiovascular risk factors and competing risks of dementia may result in counterintuitive associations, even if CVD and dementia share the same risk factors.[75–77] This has challenged the field, and more research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms behind dementia risk reduction.[38] Nevertheless, the literature on risk factors for dementia is massive; therefore this review primarily describes data from meta-analyses for all-cause dementia, for AD, and/or for vascular dementia (VD).
Diabetes. A strong association between diabetes and increased risk of dementia is reported in several meta-analyses with relative risks in the range of 1.47–1.73[78–80] for all-cause dementia, 1.33–1.56[4,79–82] for AD, and 2.27–2.38[79,80] for VD. The association between diabetes[83–88] or glycated haemoglobin levels[87,89] and dementia has not been supported by Mendelian randomization (MR) studies, although three studies reported a suggestive genetic association between higher fasting glucose,[83] higher plasma glucose,[90] or decreased insulin sensitivity[85] and higher risk of dementia. Metabolic oxidation products associated with hyperglycaemia have been identified in senile plaques from post-mortem examinations of AD patients,[91] indicating that at least hyperglycaemia could play a role in AD. The mechanism for the association with VD is probably through vascular pathology, as Type 2 diabetes and hyperglycaemia are shown to cause both macro- and microvascular complications,[1,2,92–96] general cerebral atrophy, and increased permeability of the blood–brain barrier.[1,69,96,97]
Hypertension. Midlife hypertension has recently been reported to be associated with increased risk of AD in three meta-analyses with relative risks ranging from 1.18 to 1.61.[4,98,99] Ou et al.[98] reported a relative risk of all-cause dementia of 1.20 (1.06–1.35). Three meta-analyses reported associations with decreased risk of all-cause dementia and AD in hypertensive individuals treated with antihypertensive drugs, with relative risks ranging from 0.79 to 0.88 for all-cause dementia[98,100,101] and from 0.81 to 0.84 for AD.[98,100,101] The increased risk of all-cause dementia and AD is thought to be through increased risk of cerebrovascular disease[99] and possibly also the metabolic syndrome.[1,2] Mendelian randomization studies on hypertension suffer from pleiotropic effects of the genetic instrument, and thus the potential causality of the association is difficult to interpret.[83,84,89,102]
Smoking. Strong evidence associates current smoking with increased risk of cognitive decline and dementia in several meta-analyses. Reported relative risks of all-cause dementia are between 1.27–1.59,[4,103–105] for AD relative risks of 1.40–1.79[103,105] are reported, and for VD 1.38–1.78[103,105] are reported. Heavy smoking is reported to be associated with further increased risk of all-cause dementia.[103] The association between smoking and all-cause dementia remains after adjusting for death as a competing risk,[106] which is important since smoking also associates with premature death before the age where dementia occurs. It is further shown that smoking cessation, even at high age, is associated with reduced risk of all-cause dementia.[107] Mendelian randomization studies generally have weak instruments only using one to four single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs).[83,84,108,109] Three studies reported a suggestive causal relationship between smoking quantity (using rs1051730[110]) and risk of AD but in opposite directions.[83,84,109] One of the studies further reported a genetic association between the same SNP and all-cause dementia.[109] It is assumed that the association of smoking with dementia risk is due to cardiovascular pathology or due to the content of neurotoxins in cigarette smoke.[111]
Physical Activity. Two meta-analyses reported an increased risk of all-cause dementia associated with lower physical activity with a relative risk of 1.40 (1.23–1.71)[112] and increased risk of AD with relative risks of 1.36–1.82.[4,112] Several large meta-analyses of primarily prospective cohort studies found high physical activity to be associated with decreased risk of cognitive decline[113] and all-cause dementia[4,112,114–116] in previously non-demented individuals. High levels of exercise were found to be associated with the strongest protective association in two meta-analyses, with relative risks of 0.62 (0.54–0.70) for cognitive decline,[113] 0.72–0.80 for all-cause dementia,[114,116] 0.55–0.86[104,114,116] for AD, and 0.79 (0.66–0.95) for VD.[116] By restricting analyses to physical activity measured ≥20 years before follow-up, Iso-Markku et al.[116] reported relative risks of 0.79 (0.71–0.87) for all-cause dementia and 0.76 (0.64–0.90) for AD associated with high levels of exercise. Associations were not affected by adjustment for APOE ɛ4, baseline cognition, or education.[116] Assessed via PubMed, we only found two MR studies examining a potential causal relationship between objectively measured physical activity and risk of all-cause dementia or AD, and neither of them reported a suggested causal association.[89,117] The genetic instruments for physical activity are generally weak, the two studies used three[89] and eight SNPs,[117] respectively. Nevertheless, recent robust studies suggest that moderate to high physical activity, especially in midlife, is associated with decreased risk of all-cause dementia[1,2,106,116,118–120] and that physical activity in leisure time has a stronger influence on risk of dementia than physical activity at work.[120] The biological mechanisms behind the impact of physical activity is not clear but assumed to be indirect through the modification of other joint dementia and cardiovascular risk factors,[112–114] e.g. by lowering blood pressure, and inflammatory markers and possibly prevent obesity and diabetes.[121,122] Physical activity is also suggested to attenuate age-related decline in cerebral blood flow and induce neurogenesis within the hippocampus.[123,124] Furthermore, the observation of a consistent relationship between observed maximal oxygen uptake and cerebral blood flow confirms that the benefits of aerobic exercise are not limited to the cardiovascular circulation but can be extended to the cerebrovascular circulation.[123,124]
Physical activity might also have neurotrophic effects yielding angiogenesis, synaptogenesis, and neuronal growth and survival, possibly leading to increased brain plasticity and cognitive reserve and maintained blood–brain barrier integrity.[113,114,123–125]
Midlife Obesity. Obesity is defined as a body mass index (BMI) of at least 30 kg/m2.[126] In meta-analyses, midlife obesity is reported to be associated with increased risk of all-cause dementia with relative risks in the range of 1.33–1.93[127–130] and AD in the range of 1.59–2.04.[4,81,82,129] Mendelian randomization studies do, however, not suggest that these associations are of a causal nature.[83,84,89,131–133] Interestingly, an extended MR study by Brenowitz et al.[134] found that a polygenic risk score (PRS) for AD reduced BMI by age 50, supporting the notion that low BMI is a consequence rather than a cause of dementia.
Education. Low educational attainment, corresponding to a maximum of finalized primary school, is the modifiable risk factor that most consistently associate with higher risk of dementia shown in several meta-analyses[4,104,135,136] with relative risks for all-cause dementia in the range of 1.59–1.99,[104,135,136] for AD of 1.59–1.80[4,135] and for non-Alzheimer's dementias of 1.32 (0.92–1.88).[135] A MR study using 152 SNPs associated with educational attainment showed a genetic association between higher educational attainment and lower risk of AD with an odds ratio of 0.89 (0.84–0.93) per year of completed education.[84] The genetic association was replicated in another study using 112 SNPs with no reported pleiotropy.[137] A third large MR study, using 148 SNPs associated with educational attainment and 180 SNPs associated with intelligence, found the genetic association between educational attainment and AD risk largely mediated by the influence of educational attainment on later intelligence.[138] The potential causal relationship is supported by findings of shared genetics between AD and multiple measures of educational attainment.[63] The mechanism is not clear; one theory is that educational attainment simply is a surrogate measure for higher socioeconomical status and a healthier lifestyle.[104] Another theory is that higher educational attainment leads to higher cognitive reserve,[139,140] where education has direct impact on the brain structure by increasing synapse number and/or expanding the vascular network.[104] Hence, a larger neuropathological burden is necessary for individuals with higher educational attainment to develop clinical dementia.[141,142] Two meta-analyses reported an association between higher educational attainment and higher risk of rapid cognitive decline once the dementia diagnosis was established.[142,143] This rapid cognitive decline is most likely caused by a higher neuropathological load in individuals with high cognitive reserve when the dementia diagnosis is established.
Other Risk Factors. Traumatic brain injury is suggested to increase risk of dementia through increased levels of amyloid-β as observed in animal studies.[2] Hearing impairment was reported with the highest population attributable fraction by the Lancet Commission 2020 Report on Dementia, partly because of the high prevalence in the population. Cognition decreased with every 10 dB reduction in hearing, and midlife hearing impairment is associated with a steeper temporal lobe volume loss, including the hippocampus and entorhinal cortex. Hearing aid use was reported to protect from cognitive decline.[2] Several psychiatric disorders and the corresponding treatments have shown associations with dementia, e.g. depression and social isolation, anxiety, and bipolar disorder. However, the direction of causal inference is not clear. Air pollutants as nitrogen dioxide (NO2), carbon monoxide (CO), and fine ambient particulate matter (PM)2–5 are associated with increased incidence of dementia, suggestively through cerebrovascular disease and CVD, amyloid-β, and APP processing.[2] In general, more research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms behind dementia risk reduction through these modifiable risk factors and importantly also to clarify the contribution of ethnicity.[38] The association between excessive alcohol consumption and cognitive impairment and dementia is well established and is strongest in early-onset dementias (age <65 years)[2] and is therefore not detailed in this review on late-onset dementia.
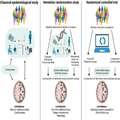
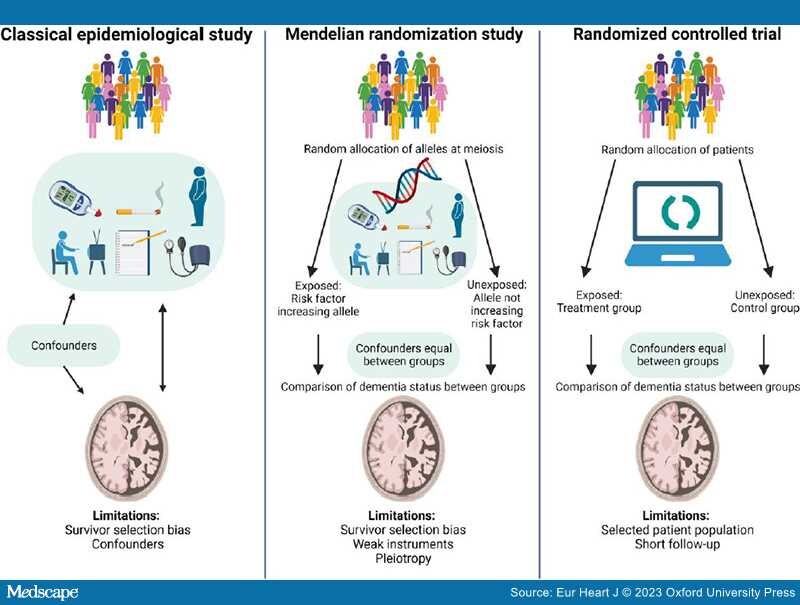
Limitations of Observational and Mendelian Randomization Studies. Survivor selection bias and confounding are inherent limitations of observational studies.[75] Survivor selection bias is of special concern in both observational and genetic cross-sectional case-control studies because this design only illustrates frequency differences of risk factors among cases and controls and therefore may produce counterintuitive associations between risk factors and dementia.[75–77] By using MR studies where we take advantage of the random assortment of alleles at conception and the fact that genes are not changeable by lifestyle factors, confounding can be circumvented[144,145] (Figure 2). This design thus mimics the randomization process in randomized controlled trials (RCTs). In contrast to the shorter follow-up in RCTs (months/years), the MR study estimates life-long effects of the exposure. However, a critical assumption of the MR design is that the genetic instrument should influence risk of disease only through the exposure of interest (no pleiotropy). To increase power, the two-sample MR design, using summary-level data from two different populations, one for the exposure and one for the outcome, can be applied. However, these populations very often consist of selected samples of patients and controls and therefore may not be representative of the general population.
Figure 2.
Modifiable risk factors in dementia. In classical epidemiological studies, confounding factors, influencing both the exposure and the outcome, may bias the association between the exposure and the outcome. Therefore, the associations identified in classical epidemiological studies cannot suggest causality. Mendelian randomization studies simulate a randomized controlled trial because genetic variants are randomly assorted at conception and not changeable by lifestyle factors or disease, and hence confounders can be assumed to be equally distributed between risk factor groups. Observational and genetic studies suffer from survivor selection bias, most pronounced in case-control studies. Design specific limitations are mentioned in the figure and described in the text in 'Limitations of observational and Mendelian randomization studies' on pages 10–11. Figure created with biorender.com.
As mentioned above, an important limitation to all observational and MR studies is survivor selection bias that may generate potentially misleading associations.[75–77] The key to circumvent survivor selection bias is to include individuals as young as possible, long follow-up, and adjustment for competing risks of death. In MR studies, multivariable MR (adjusting for the genetic contributions from common causes of survival and outcome) is a method to manage survivor selection bias and competing risk bias.[76,77] The meta-analyses included in this review primarily consist of prospective cohort studies with generally healthy individuals at baseline and especially cognitively healthy individuals. The bias sources inherent in cross-sectional studies should therefore to some extent be avoided in the present review.
Risk Prediction in Dementia
In contrast to dementia, risk scores in CVD have been implemented clinically decades ago, exemplified by the Systematic Coronary Risk Estimation (SCORE).[146] These risk scores include environmental or acquired causal risk factors such as age, sex, smoking, systolic blood pressure, and total cholesterol or non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol.[146–148] Although the first common genetic variants associated with common diseases were identified over 20 years ago, polygenetics is still not a part of risk stratification in the clinic.
Risk Scores in Dementia. In dementia research, the disappointing results from RCTs have further encouraged the development of usable risk prediction tools for primary prevention.[149] Several risk scores have been generated over the past decades.[106,150–180] They have consistently replicated associations with clinical AD, all-cause dementia, and mild cognitive impairment, with age at onset, and with biomarkers and magnetic resonance imaging measurements associated with AD such as cerebrospinal fluid levels of amyloid-β, hippocampal volume, and white matter lesions. Generally, the risk scores can be divided into three categories: risk scores only assessing genetics,[150–171] risk scores only assessing modifiable factors,[172–176] and risk scores assessing a combination of the two.[106,177–180] The risk scores assessing genetics primarily generate PRS. Polygenic risk score has the advantage of being independent of age and conventional risk factors, and since genes do not change during the lifespan, each individual only needs one assessment of genetic risk.[149,181] Polygenic risk score could especially be useful in primary prevention of diseases of mid- and late life with prodromal phases spanning over decades, such as dementias, because it makes it possible to initiate preventive interventions in high-risk individuals before pathophysiological processes have initiated.[182,183] Because of the highly increased risk of the APOE ɛ4 allele compared to the remaining known AD-associated variants, APOE is mostly assessed separately and thereby not included in the PRS in the studies including several AD-associated variants. The included modifiable risk factors are primarily cardiovascular risk factors and educational attainment, and the modifiable risk factors are mainly assessed by scoring systems summing up points from the different risk factors included in the score. Half of the studies included in this review reported predictive probabilities of the generated risk scores. Risk scores only assessing genetics reported areas under the curve (AUC) ranging from 62% to 82% for AD.[150–152,161,163,168] One risk score assessing only modifiable risk factors yielded an AUC of 74.7% for all-cause dementia.[176] When combining genetics and modifiable risk factors, AUC was 81.2% for AD[179] and 77.6%–81% for all-cause dementia.[177,179,180] Harrell's concordance statistics (c-statistics) ranged from 0.676 to 0.803 for AD risk scores only assessing genetics,[160,166] whereas risk scores only assessing modifiable risk factors reported c-statistics between 0.63 and 0.736 for all-cause dementia.[173,175,176] When combining genetics and modifiable risk factors, one risk score reported a c-statistics of 0.895 for both AD and all-cause dementia.[106]
Only six studies calculated future risk of dementia assessing competing risk of death by other causes than dementia.[106,154,157,167,173,174] It is critical to take competing risk of death into account when assessing diseases of late life to avoid overestimation of the event of interest.[184] Two of the six studies only included modifiable factors; one study tested the predictive performance of three established cardiovascular risk scores,[173] whereas the other assessed risk factors that are self-reportable or easily identifiable in a primary care setting such as age, sex, marital status, hypertension, depression, and hearing loss.[174] Three of the six studies included only genetics; one assessing 10-year absolute risk of dementia restricted to APOE genotype,[167] while the other two studies further included a PRS of 23 AD-associated SNPs on two different cohorts.[154,157] The sixth study accounting for competing risk of death presented 10-year absolute risk of dementia combining cardiovascular risk factors, education, age, sex, and genetic variants.[106]
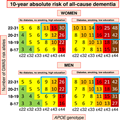
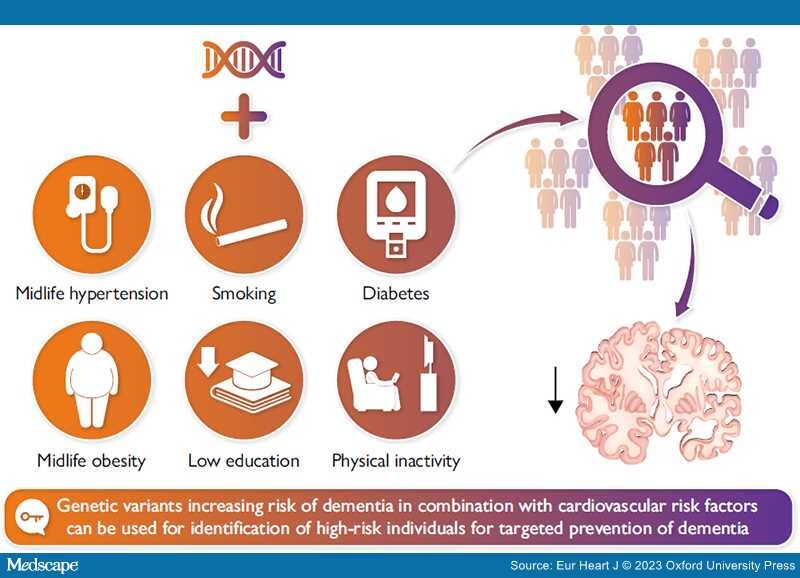
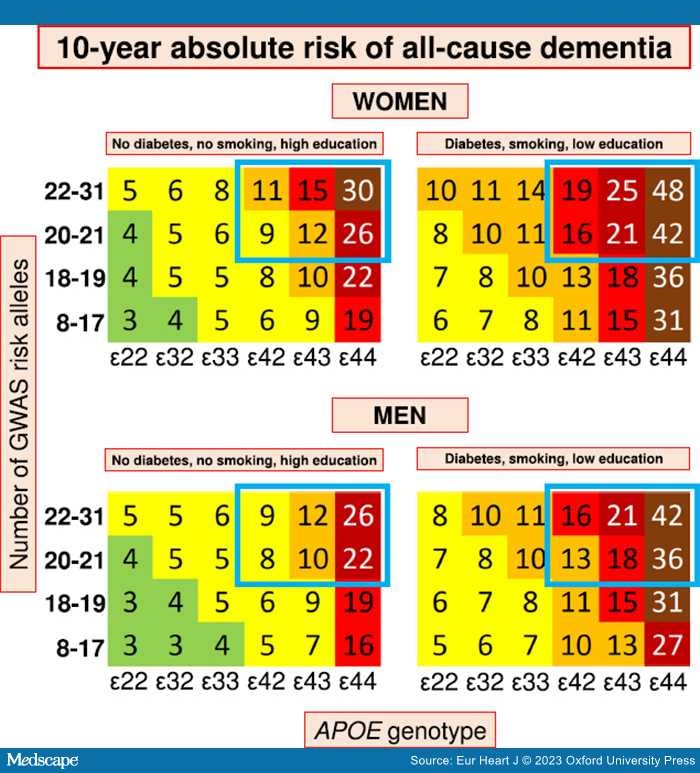
The four studies including genetics and accounting for competing risk of death confirmed APOE ɛ4 and age as major risk predictors of AD and all-cause dementia in three separate prospective cohorts of the general Danish,[106,167] Dutch,[154] and Australian and American population.[157] Three studies had follow-up from young adulthood and found cumulative incidences of dementia >60% in individuals homozygous for APOE ɛ4 and above 85 years old.[106,154,167] Van der Lee et al. further showed that PRS generated from common variants significantly predicted risk of AD, all-cause dementia, and age at onset. The risk was further increased as a function of APOE genotype.[154] Juul Rasmussen et al.[106] combined cardiovascular risk factors, education, age, sex, and genetic variants associated with AD and generated 10-year absolute risk charts for all-cause dementia and AD in a large, prospective cohort of 61 664 individuals. The presentation is similar to the widely used SCORE[146] and the newly updated SCORE2[147] and SCORE2-OP[148] for risk of CVD to make it easily applicable in a clinical setting.[106] The genetic risk score included 19 common SNPs, associated with increased risk of AD,[64] in a simple allele score divided into four categories in addition to the strong APOE genotype. The 10-year absolute risk was further stratified by sex and up to three cardiovascular risk factors and showed that a healthy cardiovascular lifestyle attenuates genetic susceptibility for all-cause dementia up to 41% in individuals homozygous for APOE ɛ4 and above 70 years of age.[106] Overall, a healthy cardiovascular lifestyle almost halves the risk of dementia across all age groups and genetic risk in both sexes[106] (Figure 3). From a clinical perspective, it is probably sufficient for AD prediction to include genome-wide statistically significant genetic variants[185] due to the major impact of common variants in APOE, in contrast to what has been suggested for CVD.[186]
Figure 3.
Summary figure of 10-year absolute risk of all-cause dementia in individuals 70–79 years of age stratified by modifiable risk factors, APOE genotype, and GWAS risk alleles. Ten-year absolute risk is read by identifying the person's sex, their diabetes, smoking, and educational status, their APOE genotype, and their number of GWAS risk alleles. 10-year absolute risk of dementia is given in percentage. Among individuals with the highest genetic risk (blue framing), 10-year absolute risk of all-cause dementia increased 60%–80% depending on the burden of cardiovascular risk factors. Colour code: light green 1%–4%; yellow 5%–9%; orange 10%–14%; red 15%–19%; dark red 20%–29%; brown ≥30%. APOE, apolipoprotein E gene; APOE genotype, ɛ2/ɛ3/ɛ4 APOE genotype; GWAS, genome-wide association study. Complete figures on 10-year absolute risk of all-cause dementia in women and men are available as Figure 2 and Figure 3 in the credit article. Credit: Juul Rasmussen et al., Impact of cardiovascular risk factors and genetics on 10-year absolute risk of dementia: risk charts for targeted prevention, Eur Heart J, 2020, 41, 41, 4024–4033, by permission of the European Society of Cardiology.
Perspectives
Over the past decades, GWAS studies have identified 75 loci associated with AD.[63–65] GWAS studies are designed to identify common variants that most often have small effect sizes on the disease or trait of interest.[20,21] These small effect sizes are usually too weak to use as a proof for a novel robust drug target. From other common diseases, like CVD, effective drug targets have been discovered in pedigrees with a rare genetic variant with larger effect size as the PCSK9 gene variant identified in familial hypercholesterolaemia.[183,187]
In 2019, a somewhat similar case was described for AD: a member of a family carrying a PSEN1 mutation developed cognitive symptoms 30 years later than family members carrying the same mutation.[188] On neuroimaging, the proband displayed remarkably high amounts of senile plaques but sparse tau pathology.[188] The proband turned out to be carrying a possible drug target, as she was homozygous for a rare mutation in APOE, called APOE3 Christchurch[189,190] affecting the binding of apoE to heparan sulfate proteoglycans.[190] Heparin-binding affinities of apoE isoforms are apoE4 > apoE3 > apoE2 > apoE3christchurch, and lower binding affinity is suggested to decrease neuronal tau pathology, hence decreasing AD pathology.[191,192] Together with a recent report of low AD risk and sparse tau pathology in APOE ɛ22 carriers,[192] this observation proposes a potential drug target. Monoclonal antibodies inhibiting the binding of apoE to heparin have been developed and appear protective against tau pathology in neurons in in vitro studies.[188] Importantly, when designing future dementia RCTs, it will be crucial to include the most suitable individuals. In the case of a heparin-binding inhibitory antibody, the first choice would be to stratify potential participants by their APOE ɛ4 status. Since the effect is expected to block or slow down the neuronal uptake of tau and not to remove already established pathology, non-demented individuals would be most eligible, making a risk score like the one suggested by Juul Rasmussen et al.[106] obvious to use in the inclusion phase.
In a public health perspective, prevention is more important than treatment, and it is suggested that a 10% reduction in prevalence of cardiovascular risk factors could prevent more than nine million AD cases worldwide by 2050.[4] This assumes causality between cardiovascular risk factors and AD and adherence to the interventions over decades for a large number of individuals.[4,193] In causal inference of risk factors and AD, new methods are needed that overcome the problems with survivor selection bias observed in all observational studies including GWAS. One such method is suggested to be multivariable MR.[77] In dementia, preventive intervention trials have clarified that intensive multidomain interventions are required to decrease risk of dementia,[22–25] and through post hoc analyses, it is clear that face-to-face contacts with, e.g. nurses or physiotherapists, are required for maintaining adherence.[194] This emphasizes the importance of risk stratification to include individuals at highest risk who presumably will benefit the most from costly interventions. Risk stratification will further enable targeted interventions in high-risk individuals before dementia pathophysiology is established, decades before symptom debut. To the best of our knowledge, there are still no intervention studies primarily focusing on middle-aged, cognitively healthy individuals.
Eur Heart J. 2023;44(28):2526-2543. © 2023 Oxford University Press
Copyright 2007 European Society of Cardiology. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved.